ELK Stack : Get Started with Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana, & Beats
Introduction
Elastic Stack, formerly known as the ELK stack, is a popular suite of tools for ingesting, viewing, and managing log files. As open-source software, you can download and use it for free (though fee-based and cloud-hosted versions are also available).
Prerequisites
- A system with Elasticsearch installed
What is ELK Stack?
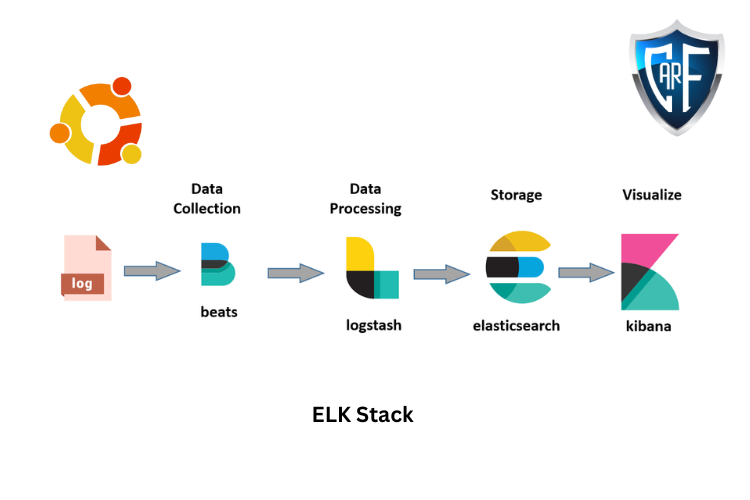
ELK stands for Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana. In previous versions, the core components of the ELK Stack were:
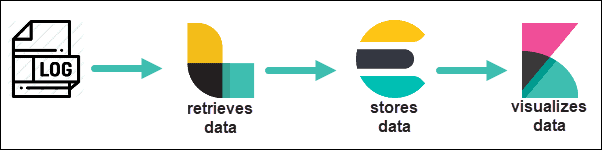
- Elasticsearch – The core component of ELK. It works as a searchable database for log files.
- Logstash – A pipeline to retrieve data. It can be configured to retrieve data from many different sources and then send it to Elasticsearch.
- Kibana – A visualization tool. It uses a web browser interface to organize and display data.
Additional software packages called Beats are a newer addition. These are smaller data collection applications, specialized for individual tasks. There are many different Beats applications for different purposes. For example, Filebeat is used to collect log files, while Packetbeat is used to analyze network traffic.
Due to the ELK acronym quickly growing, the Elastic Stack became the more satisfactory and scalable option for the name. However, ELK and Elastic Stack are used interchangeably.
Why Use ELK Stack?
The ELK stack creates a flexible and reliable data parsing environment. Organizations, especially ones with cloud-based infrastructures, benefit from implementing the Elastic stack to address the following issues:
- Working on various servers and applications creates large amounts of log data, which is not human-readable. The ELK stack serves as a powerful centralized platform for collecting and managing unstructured information, turning it into useful assets in the decision-making process.
- The ELK stack with basic features is open source, which makes it a cost-efficient solution for startups and established businesses alike.
- The Elastic stack provides a robust platform for performance and security monitoring, ensuring maximal uptime and regulation compliance.
The Elastic stack addresses the industry gap with log data. The software can reliably parse data from multiple sources into a scalable centralized database, allowing both historic and real-time analysis.
How Does Elastic Stack Work?
The Elastic stack follows certain logical steps, all of which are configurable.
1. A computer or server creates log files. All computers have log files that document events on the system in a hard-to-read format. Some systems, such as server clusters, generate massive amounts of log files.
However, Elastic Stack is designed to help manage scalable amounts of data.
2. The various available information files are collected by a Beats application. Different Beats reach out to different parts of the server, read the files, and ship them out.
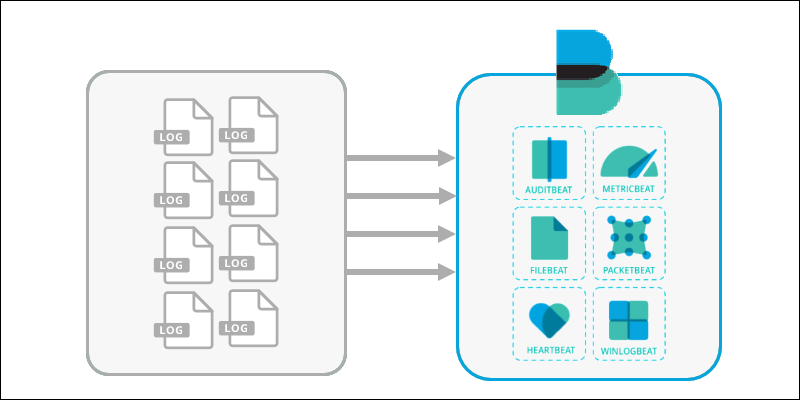
Some users may skip Beats altogether and use Logstash directly. Others may connect Beats directly to Elasticsearch.
3. Logstash is configured to reach out and collect data from the different Beats applications (or directly from various sources).
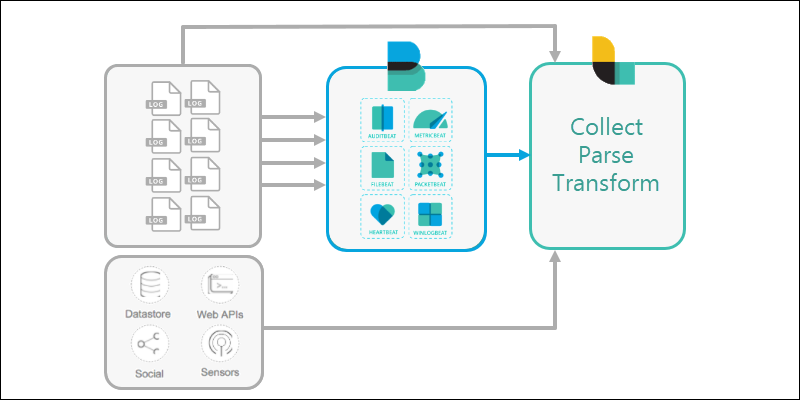
In larger configurations, Logstash can filter data from multiple systems, and collect the information into one location.
4. Elasticsearch is used as a scalable, searchable database to store data. Elasticsearch is the warehouse where Logstash or Beats pipe all the data.
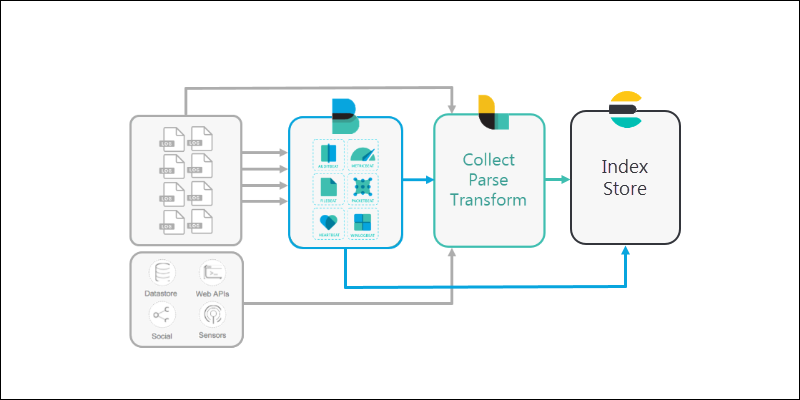
5. Finally, Kibana provides a user-friendly interface for you to review the data that’s been collected.
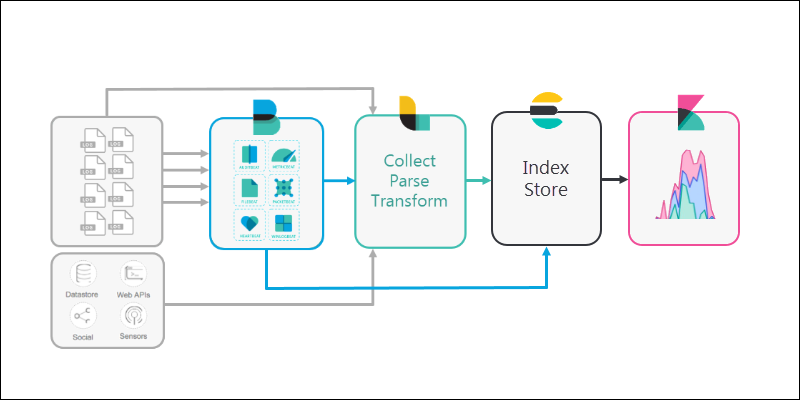
It is highly configurable, so you can adjust the metrics to fit your needs. Kibana also provides graphs and other tools to visualize and interpret patterns in the data.
ELK Stack Supporting Applications
Additional third-party applications enhance the Elastic Stack, providing wider use-case possibilities. Some external applications supported by the ELK stack are:
- Apache Kafka
Kafka is a real-time streaming distribution platform. That means that it can read multiple data sources at once. Kafka acts as a data buffer and helps prevent data loss or interruption while streaming files quickly
- Redis
Redis is a NoSQL key-value database with incredible read/write speeds and various data types. When added to the Elastic stack, Redis often serves as a buffer for data stream spikes, ensuring no data is lost.
- Hadoop
Hadoop is a massive batch-processing data storage system. Indexing data from Hadoop into the real-time Elasticsearch engine creates an interactive bi-directional data discovery and visualization platform.
The Hadoop support comes through the Elasticsearch-Hadoop Connector, offering full support for Spark, Streaming, Hive, Storm, MapReduce, and other tools.
- RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is a messaging platform. Elastic Stack users use this software to build a stable, buffered queue of log files.
- Nginx
Nginx is best known as a web server that can also be set up as a reverse proxy. It can be used to manage network traffic or to create a security buffer between your server and the internet.
ELK Stack Advantages and Disadvantages
The Elastic stack comes with certain benefits and drawbacks.
Advantages
- The Elastic stack and the components are free to try out and use.
- ELK offers numerous hosting options, whether on-premises or deployed as a managed service.
- The capability to centralize logging from complex cloud environments allows advanced searches and creating correlations from multiple sources on a single platform.
- Real-time analysis and visualization decrease the time taken to discover insights, enabling continual monitoring.
- Client support for multiple programming languages, including JavaScript, Python, Perl, Go, etc.
Disadvantages
- Deploying the stack is a complex process and depends on the requirements. Check out our tutorial for deploying the Elastic stack on Kubernetes.
- Growing and maintaining the ELK stack is costly and requires computing and data storage based on the data volume and storage time.
Related Post
 Jan 9, 2023
Jan 9, 2023
What is Threat Intelligence ?
Cybersecurity is a complex and constantly evolving field. As threats change, so must the way we approach them. One of the most essential tools in any cybersecurity practitioner’s toolkit is threat intelligence.What is Threat Intelligence?Threat intelligence is a critical component of effective cyber defense. It’s an ongoing process that requires the collaboration of many different teams and organizations, including security operations centers (SOCs), threat research teams, network engineering, and forensics experts.TI can be used in three primary ways: Identify cyber threats and vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Detect suspicious behavior within your network and respond quickly if an attack occurs. Improve the overall security posture of your organization by helping you prioritize your efforts based on accurate threat information and analysis.Why is Threat Intelligence Important?Threat intelligence sheds light on the unknown by helping security professionals understand how an adversary operates, their intentions, and how they intend to carry out their objectives.Threat intelligence helps you better understand the adversary’s decision-making process so that you can prevent attacks from happening in the future.Threat intelligence empowers business stakeholders – including executive boards, CISOs, CIOs, and CTOs – with the information they need to make informed decisions based on data rather than speculation or assumptions about an attack’s likelihood or impact.Who Benefits from Threat Intelligence?A good threat intelligence program provides value to a wide range of stakeholders. Here’s a list of some of the key groups that can benefit from threat intelligence:IT security professionalsIT security managers and directorsChief information security officers (CISOs)Chief information officers (CIOs)Chief executive officers (CEOs)The Lifecycle of Threat IntelligenceIn the past, cyberattacks were limited to a small number of computers located in one country. Nowadays, however, attacks are much more widespread and can be launched from anywhere in the world. As a result, it’s becoming increasingly difficult for security teams to keep track of all the latest threats and stay on top of them quickly enough before they cause any damage.This is where the threat intelligence lifecycle comes in handy: it’s a comprehensive framework that organizes all different aspects of threat intelligence processes into six stages (direction, collection, processing, analysis & dissemination) so you can focus on what matters most for your organization’s needs.DirectionThe threat intelligence lifecycle begins with establishing which assets and business processes need protection the most.Determine the threat intelligence objectives.Set the threat intelligence strategy.Set the threat intelligence mission, vision, and goals.CollectionThreat intelligence data helps you understand and proactively protect your organization from cyber threats. It includes data, such as known malicious IP addresses, domain names, email addresses, and other indicators of compromise (IOCs) that can be used to block or detect malicious activity. You can collect threat intelligence by using various methods, including:Feeds – These are automated notifications sent by feed providers when new IOCs are identified or existing IOCs change in status (e.g., become active again).Databases – These contain manually curated datasets of IOCs maintained by researchers or organizations like ours at Cyber Sainik.Dashboards – These pull together multiple types of threat data into one interface so you can quickly identify potential threats to your organization’s infrastructure and act on them accordingly.AnalysisNext, you will analyze your data. This step is where you find patterns and make sense of what’s going on in your environment. Look for modules that allow you to perform analysis tasks—such as pattern recognition (using machine learning), malicious behavior detection (using threat intelligence), or event correlation (connecting related ev
Read More.png) Dec 11, 2022
Dec 11, 2022
What Is Managed Detection and Response (MDR)?
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) denotes outsourced cybersecurity services designed to protect your data and assets even if a threat eludes common organizational security controls.An MDR security platform is considered an advanced 24/7 security control that often includes a range of fundamental security activities including cloud-managed security for organizations that cannot maintain their own security operations center. MDR services combine advanced analytics, threat intelligence, and human expertise in incident investigation and response deployed at the host and network levels.What challenges can Managed Detection and Response (MDR) address?As the volume, variety, and sophistication of cybersecurity threats increase exponentially, organizations struggle to maintain security operations centers staffed with highly skilled personnel and resources. As a result, Managed Detection and Response vendors provide a cost-effective menu of services designed to improve an enterprise’s cybersecurity defenses and minimize risk without an upfront cybersecurity investment.MDR services provide higher skill-level analysts utilizing cutting-edge security tools and up-to-the-minute global databases beyond the reach and cost-effectiveness of most enterprise budgets, skill levels, and resources. Thus, helping keep pace with continually evolving adversarial tactics and techniques.MDR services provide an alternative to enterprises chasing the latest in advanced security products by integrating Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools that become a challenge for security operations teams to learn and maintain. As a result, an enterprise’s level of threat monitoring, detection, and analysis is improved without the challenge and expense required to keep an internal security team fully staffed and up to date with the latest threat data.MDR services are not limited to greater detection and response capabilities. They also provide proactive defense intelligence and insight into advanced threats to potentially overwhelmed security teams. Detection levels are improved while the dwell time of breaches is reduced. Compliance challenges also can be met using MDR services providing full stakeholder reporting and log retention on a wide range of regulations and standards.Why choose Managed Detection and Response (MDR) over Managed Security Services Providers (MSSPs)?Managed Detection and Response services are often compared to Managed Security Services Provider (MSSP) services. While they share similarities, they also differ in technology, expertise, and relationship. MDR services are typically proactive and focus on threats. MSSPs are designed to be reactive and focus on vulnerabilities. Unlike MSSPs, MDR services focus on detection, response, and threat hunting rather than security alert monitoring. MSSPs manage firewalls, but do not necessarily provide the same level of threat research, analytics, and forensics as MDRs. MSSPs recognize security issues but are incapable of revealing details of the threat that MDR services provide. MSSPs use log management and monitoring, vulnerability scanning, and often Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM) platforms to notify organizations of threats. Automated MDR analytics and responses to advanced threats, file-less malware, and breaches can augment MSSP services. MDR services rely on more-direct communications such as voice or emails to analysts, rather than portals. MSSP's primary interfaces are portals and emails with secondary chat and phone access to analysts.Here are typical MDR and MSSP service comparisons. Not all MDR providers include the same levels of capabilities and tools in the following services: one.MDR ServicesMSSPs24x7 threat detection and responseSome, but not allManage firewalls and security infrastructureYesProactively managed threat hunting for unknowns on network and endpointsNoIntelligence-based threat detection, triage, and extensive forensicsNoTeam of experienced threat detection experts available via phone, email, textNoAccess to global threat intelligence and analysisNoIntegrated endpoint and network security technologyNoIn the face of seemingly overwhelming security threats and campaigns, organizations are also coping with increasing security budgets and a challenging security job market leans on skilled security analysts. Gaining more protection, insight, and compliance without adding more tools and people is a goal that enterprises of all sizes seek. MDR can provide beneficial security services capable of meeting and sustaining an organization’s goals:24/7 monitoring and improved communications mechanisms with experienced SOC analystsExperienced security analysts oversee your organization’s defenses without adding full-time staff and resourcesComplete managed endpoint threat detection and response serviceImproved threat detection and extended detection coverageExpert investigation of alerts and incidents, and subsequent actionsProactive threat huntingImproved threat intelligence based on indicators and behaviors captured from global insightsImproved threat responseDecreased breach responseImproved forensics and higher-level investigationsVulnerability managementMajor incident response and log managementRemove the burden of day-to-day security management from your staff and budgetMaintain access and customization to your organization’s security defensesImproved compliance and reportingReduced security investment, increased ROI
Read More